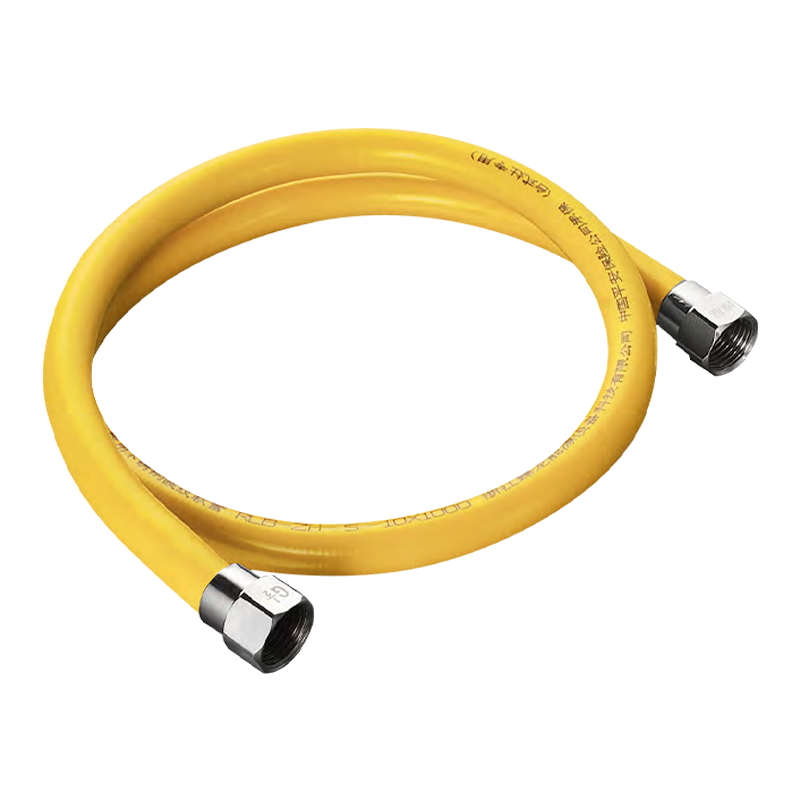
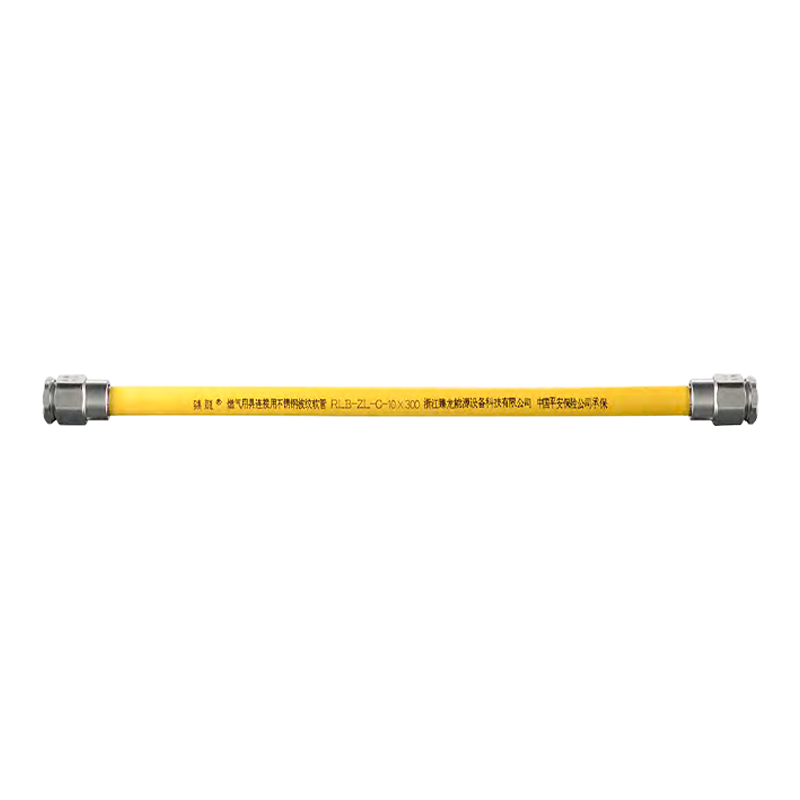
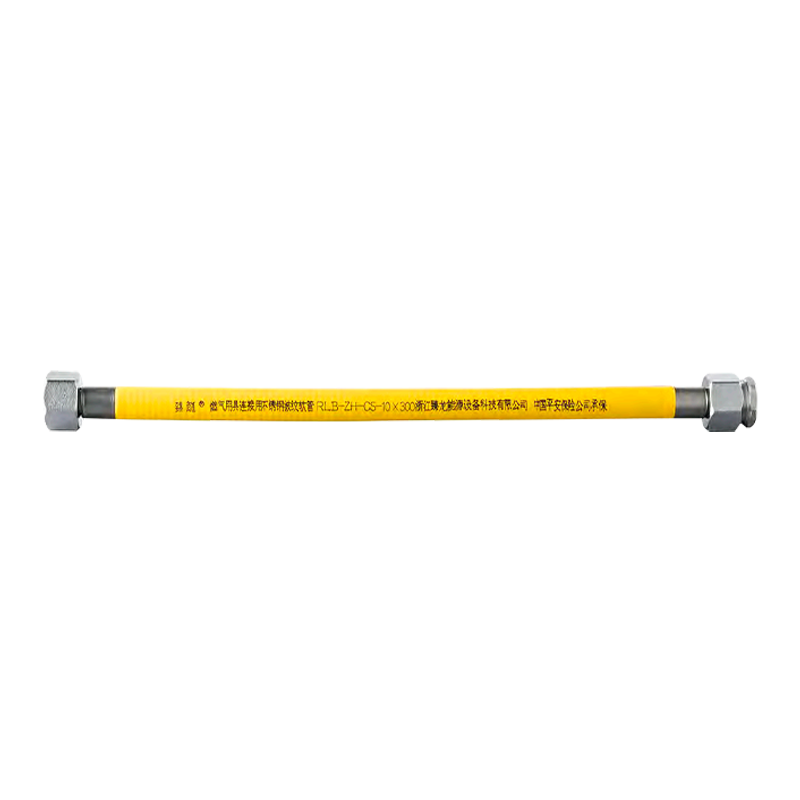
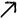Corrugated stainless steel tubing (CSST) is a flexible pipe made of 304/316 stainless steel. Its wavy surface structure combines metallic strength with flexibility. The following is a detailed explanation of its core functions, applications, and advantages:
Content
1. Functions of Corrugated Stainless Steel Tubing
- Fluid Transportation
Gas Transmission: Widely used for the transportation of combustible gases such as natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), and compressed air, replacing traditional galvanized steel pipe.
Liquid Transportation: Suitable for water, oil, and chemical media (such as weak acids and bases), with strong corrosion resistance.
- Flexible Connections and Vibration Absorption
Displacement Compensation: Absorbs stress caused by thermal expansion and contraction or mechanical vibration in the pipe, reducing the risk of leakage caused by rigid connections.
Seismic Resistance: Preferred for use in earthquake-prone areas, it can withstand a certain degree of stretching and bending deformation.
- Piping in Complex Spaces
Flexible Bendability: Eliminates the need for additional elbows and can be routed around obstacles (such as beams, columns, and equipment), simplifying installation.

2. Typical Applications
|
Industries |
Applications |
Advantages |
|
Gas Engineering |
Residential/commercial gas pipelines, gas meter back-end pipes |
Corrosion-resistant, leak-proof, and quick to install |
|
Petrochemical |
Corrosive media transportation, reactor connection pipes |
Acid and alkali resistant, high-pressure resistant (up to 10 MPa) |
|
HVAC |
Hot and cold water circulation, floor heating branch pipes |
High-temperature resistant (-50°C to 150°C), long service life |
|
Shipbuilding |
Engine fuel pipes, seawater cooling pipes |
Salt spray corrosion resistant, lightweight (70% lighter than steel pipe) |
|
Food and Pharmaceutical |
Clean fluid transportation (e.g., pure water, dairy products) |
Pollution-free, FDA-compliant |
3. Precautions for installation of corrugated stainless steel pipes
Pre-Installation Preparation
- Material Inspection
Pipe Quality: Confirm that the pipe material meets national standards and is free of indentations, cracks, or rust.
Fitting Compatibility: Use dedicated stainless steel fittings (such as crimp or threaded connections). Do not mix fittings made of other materials.
Shell Inspection: If the pipe has a PE/PVC outer covering, ensure it is intact and protected from UV or mechanical damage.
- Tool Preparation
Cutting Tools: Use a dedicated pipe cutter or stainless steel cutter. Do not use a grinding wheel (which can cause burrs).
Deburring Tools: Clean the cut with a reamer or file before installation to prevent scratching the seal.
Leak Detection Equipment: For gas pipes, soapy water or a gas detector is required.
Installation Specifications
- Cutting and Handling
Precise Measurement: Allow an appropriate margin (bending will shorten the length).
Cutting Requirements: The cut must be flat and perpendicular to the pipe axis (deviation ≤ 1°). Burrs must be removed.
Protective Measures: Immediately seal the end cap after cutting to prevent impurities from entering.
- Bending and Fixing
Minimum bend radius: ≥3 times the pipe diameter to avoid cracking caused by excessive bending.
Fixing Spacing:
Horizontal pipes: Install clamps or brackets every 1-1.5 meters.
Vertical pipes: Install brackets every 1 meter to prevent sagging.
Avoid stress concentration: Bends should be kept away from joints, and direct stress should not be applied to corrugations.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español عربى
عربى