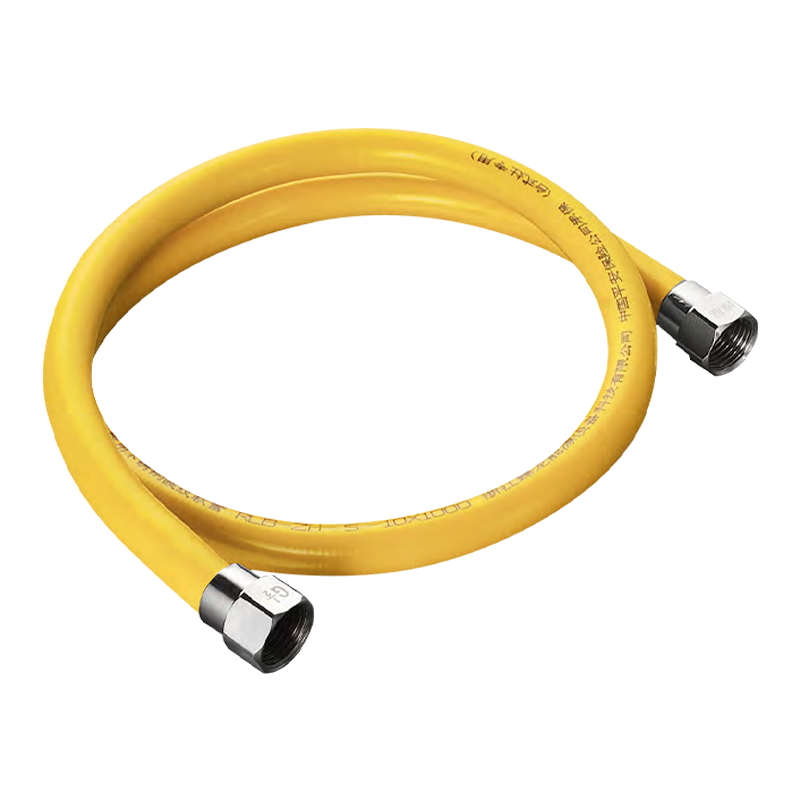
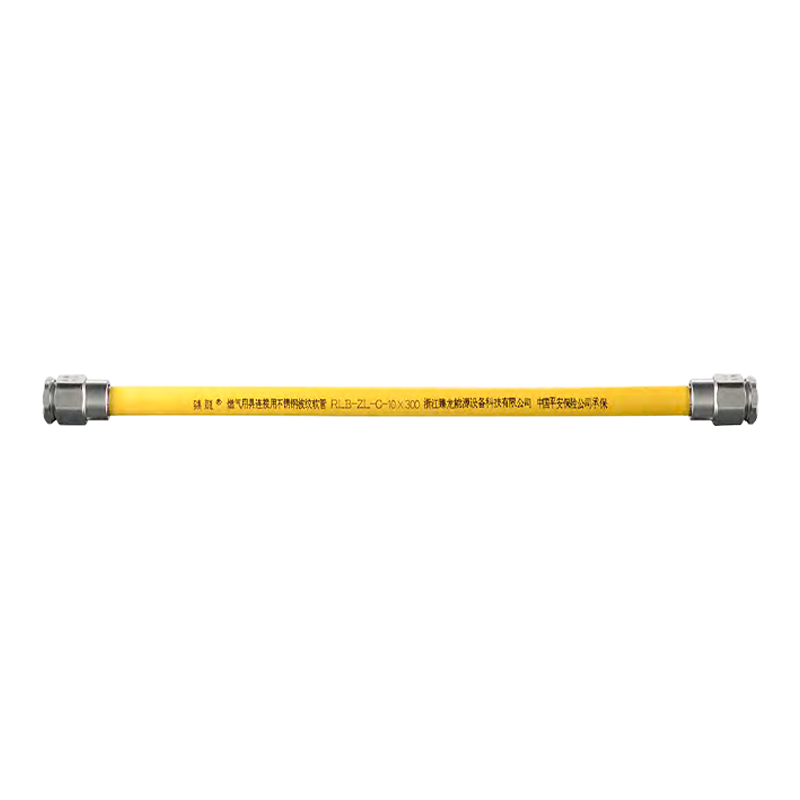
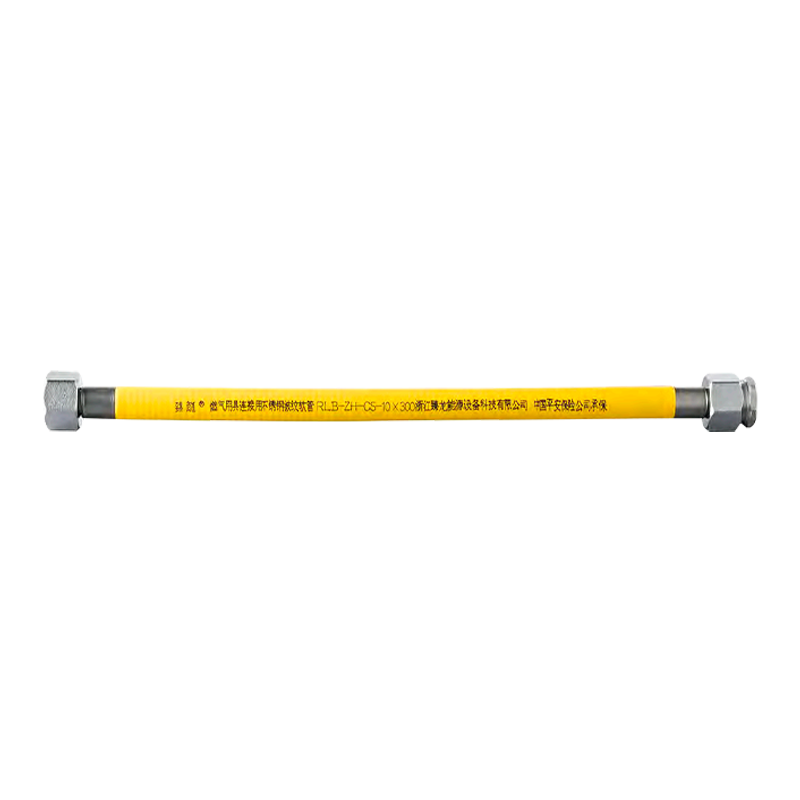
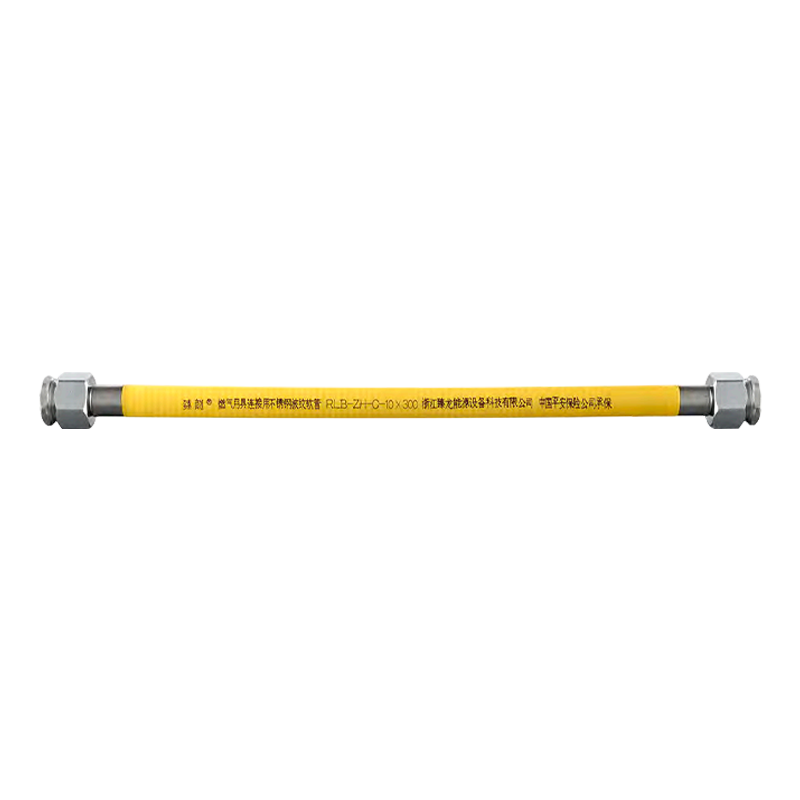
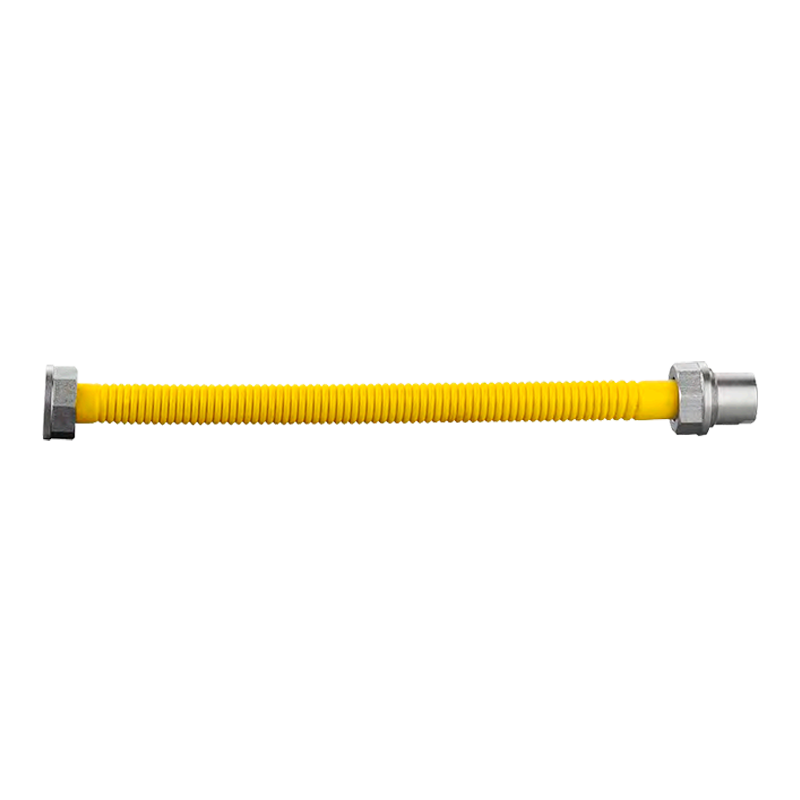
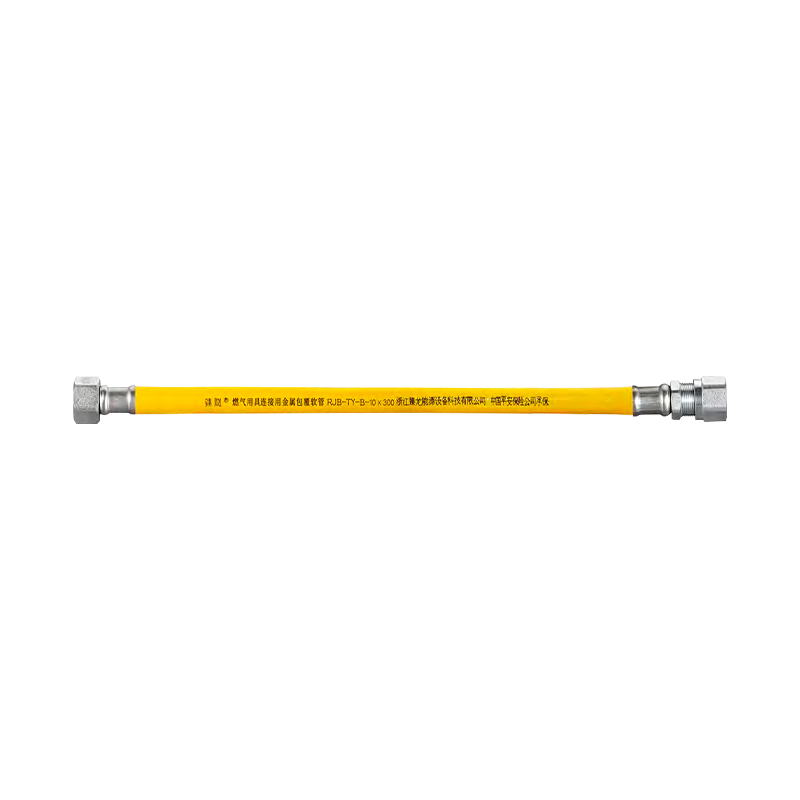
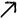Are you still using old-fashioned rubber or plastic braided hose to connect your gas stove or water heater? If so, your home could be harboring a significant safety hazard. Stainless steel corrugated hose is gradually replacing older rubber hoses. Why?
1. Improved Safety: Eliminates the Risk of Pipe Bursts
Traditional braided hoses: The rubber inner material ages, becomes brittle, and cracks after prolonged exposure to oil fumes and heat. Once cracked, gas or hot water leaks can result in devastating consequences.
Stainless Steel Corrugated Hose: The core is made of 304 stainless steel, with a flame-retardant PVC protective layer. It is corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant, and age-resistant, with a service life of 8-10 years, far exceeding the 18 months of traditional rubber hoses. This material significantly improves safety.
2. Easy Installation and High Adaptability
Despite its name, it's incredibly strong. Its unique corrugated structure acts like a spring, offering excellent resistance to pressure and bending while remaining remarkably flexible.
When installed in complex environments like narrow cabinets and corners, it can bend easily around obstacles without cutting or splicing, significantly reducing installation difficulty and the risk of leaks.
Its flexibility makes it less susceptible to breakage when subjected to external compression or tension, providing a higher safety factor.
3. Enhanced Sealing
The stainless steel bellows utilize a standard metal nut interface. Connections to gas stoves and valves are achieved through a spherical seal, providing a highly compatible seal that far surpasses the clamp-type connections of traditional hoses, effectively preventing minor gas leaks caused by loose connections.
4. Wide Range of Applications
It is not only an ideal choice for use as a gas hose, but is also ideal for:
Cold/hot water connections: For example, connecting to water heaters, toilets, and washbasin faucets, with excellent high and low temperature resistance.
Gas appliance connections: For gas stoves, wall-mounted boilers, etc.
Installation Specifications for Stainless Steel Corrugated Hose
(1). Pre-Installation Preparation
Material and Tool Inspection: Prepare a wrench, cutter, connectors (such as flanges and pipe clamps), seals, gaskets, etc. Verify that the bellows' model, specifications, pressure rating, and compensation amount meet design requirements.
Inspect the pipe surface for scratches, indentations, and other transportation damage.
Pipe System Inspection: Ensure the interior of the pipe to be connected is clean and free of foreign matter. Check the pipe support system, ensuring the position and strength of the fixing brackets and guide brackets meet the design.
Pre-Deformation Treatment (if necessary): For compensators, pre-stretch or pre-compress according to the calculated values based on design requirements and the difference between the ambient temperature and the operating temperature, and then temporarily secure them.
(2). Installation Steps and Technical Requirements
Cutting and Processing:
Measure and mark the required length. Use a dedicated cutting tool (such as a cutter) to make a perpendicular cut.
After cutting, remove burrs from the pipe ends to ensure a smooth and even cross-section. Avoid damaging seals or scratching the bellows. Connection and Tightening:
Alignment and Centering: During installation, ensure the bellows and pipe are coaxial and accurately aligned, with deviation kept to a minimum (recommended ≤1mm/m). Do not forcibly stretch, compress, or twist the bellows to adjust for pipe installation errors.
Flange Connections: Ensure the flange sealing surfaces are clean and flat. Tighten the bolts gradually and evenly, using a diagonal pattern, to prevent stress concentration. Bolts should be evenly loaded, ensuring a straight and even fit between the two flanges.
Threaded Connections: Ensure the threads are intact. Manually tighten them smoothly before tightening with tools to avoid skewing. Pay attention to the winding direction and tighten with force to avoid thread stripping.
Bending Requirements:
Stainless steel bellows can be bent, but bending directly at the base of the bellows (i.e., at the crest or trough of the wave) is strictly prohibited. Sharp bends (dead bends) should also be avoided.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español عربى
عربى