1. Comparison of commonly used materials for residential indoor gas pipelines
Galvanized steel pipe
Advantages: moderate cost, high mechanical strength, good pressure resistance, and wide traditional application.
Disadvantages: susceptible to electrochemical corrosion, requires regular maintenance, service life of about 20 years, and heavy weight.
Polyethylene (PE) pipe
Advantages: corrosion resistance, impact resistance, good flexibility, suitable for underground laying, and service life of up to 50 years.
Disadvantages: not resistant to high temperature, UV aging protection is required for open installation, and special hot melt equipment is required for connection.
Aluminum-plastic composite pipe
Advantages: Combining the characteristics of metal and plastic, corrosion resistance, light weight, suitable for open installation.
Disadvantages: The joint is easy to loosen, long-term use may delaminate, and the pressure bearing capacity is limited.
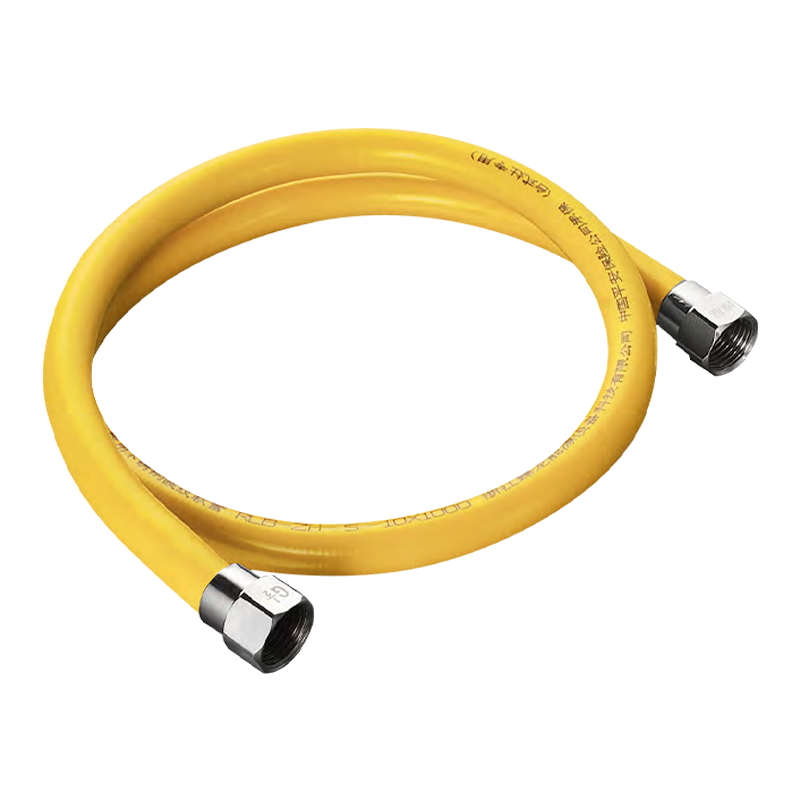
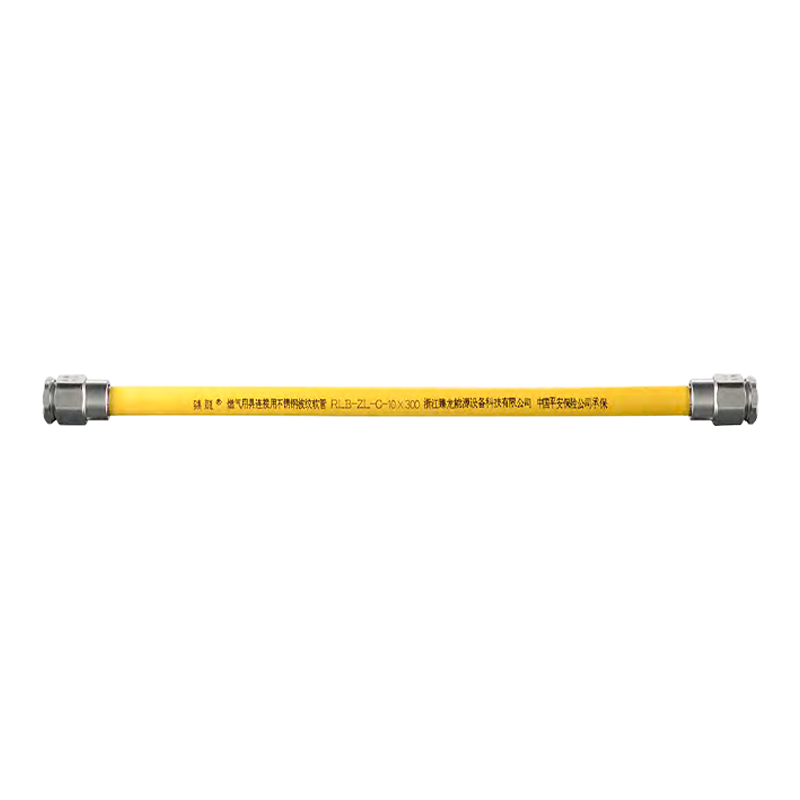
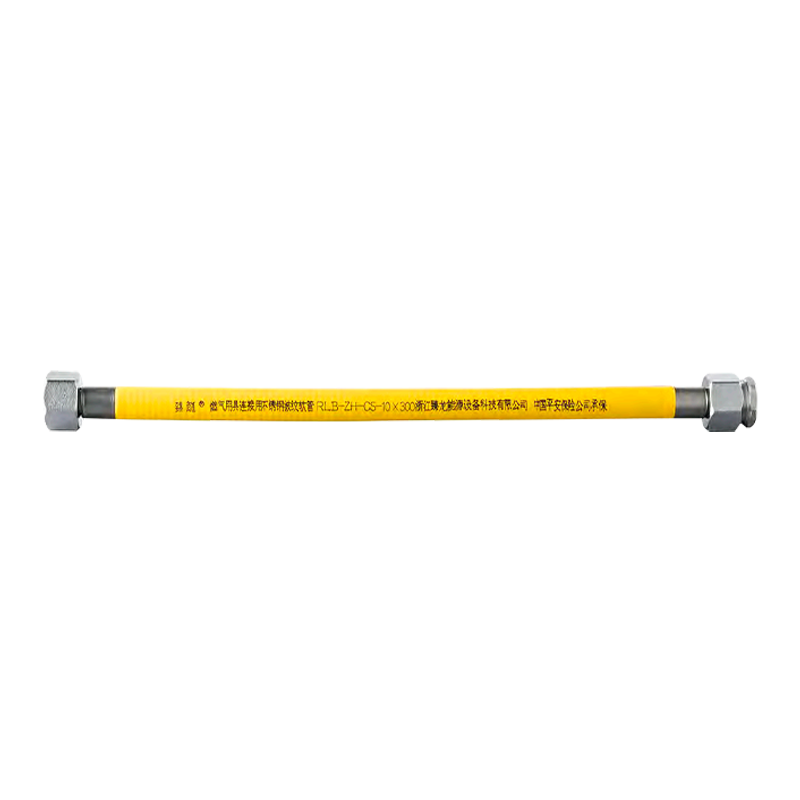
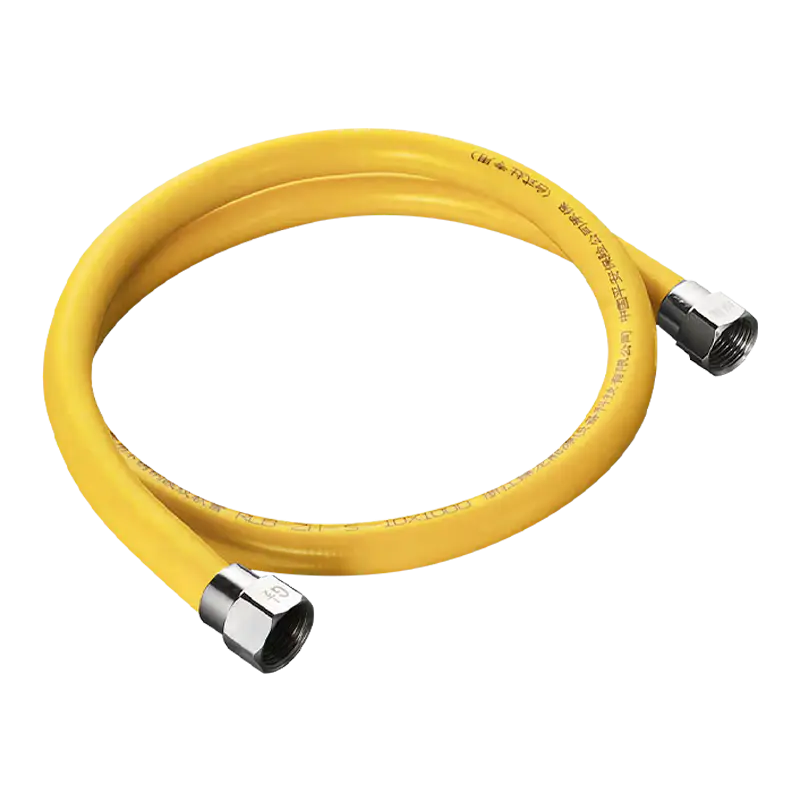
Stainless steel corrugated pipe
Core advantages:
Corrosion resistance: 304/316L stainless steel material, resistant to acid, alkali, and oil fume corrosion, with a service life of up to 50 years.
Earthquake resistance and flexibility: The corrugated structure can absorb the stress of earthquakes and building settlement, reducing the risk of leakage.
Safety performance: High temperature resistance, rat bite resistance, and compliance with the new national standard for gas safety.
Easy installation: Threaded connection prevents falling off, and no additional pipe fittings are required for bending, reducing leakage points (traditional galvanized pipes require 10-15 joints, while corrugated pipes only require 2).
Limitations: The cost is high, and repeated bending should be avoided to cause metal fatigue.

2. Key factors for pipe fitting selection
Material matching
Stainless steel corrugated pipes need to be equipped with stainless steel pipe fittings (such as double clamping joints) to ensure corrosion resistance and sealing.
PE pipes require special hot-melt or electric-melt pipe fittings to avoid interface leakage.
Connection method
Threaded connection: Applicable to stainless steel corrugated pipes, and the sealing needs to be checked.
Compression connection: Used for stainless steel pipe fittings, professional tools are required for operation to ensure plastic deformation sealing.
Hot-melt connection: Exclusive for PE pipes, temperature and pressure need to be controlled.
Specification adaptation
The pipe diameter and wall thickness need to be selected according to the gas pressure.
3. Why choose corrugated stainless steel pipe?
Corrosion resistance and long life
304/316L stainless steel is resistant to acid and alkali, oil fume corrosion, and has a lifespan of 50 years, far exceeding galvanized steel pipes (about 20 years) and rubber hoses (easy to age and crack). Surface passivation treatment further reduces the risk of corrosion and adapts to complex environments such as humidity and high temperature.
Seismic resistance and flexibility
The corrugated structure can absorb stress such as building settlement and earthquake to avoid breakage; it has good bending performance, and does not require frequent use of joints during installation, reducing leakage points.
High temperature resistance and flame retardant
Stainless steel can withstand high temperature flames, and the outer PVC protective sleeve is flame retardant to avoid secondary disasters caused by fire.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español عربى
عربى